If you’ve ever debugged a production incident, you know that the hardest part often isn’t the fix, it’s finding where to begin. Most on-call engineers end up spending hours piecing together clues, fighting time pressure, and trying to make sense of scattered data. You’ve probably run into one or more of these challenges:
- Unwritten knowledge and missing context:
You’re pulled into an outage for a service you barely know. The original owners have changed teams, the documentation is half-written, and the “runbook” is either stale or missing altogether. You spend the first 30 minutes trying to find someone who’s seen this issue before — and if you’re unlucky, this incident is a new one. - Tool overload and context switching:
Your screen looks like an air traffic control dashboard. You’re running monitoring queries, flipping between Grafana and Application Insights, checking container logs, and scrolling through traces — all while someone’s asking for an ETA in the incident channel. Correlating data across tools is manual, slow, and mentally exhausting. - Overwhelming complexity and knowledge gaps:
Modern cloud-native systems like Kubernetes are powerful, but they’ve made troubleshooting far more complex. Every layer — nodes, pods, controllers, APIs, networking, autoscalers – introduces its own failure modes. To diagnose effectively, you need deep expertise across multiple domains, something even seasoned engineers can’t always keep up with.
The challenges require a solution that can look across signals, recall patterns from past incidents, and guide you toward the most likely cause.
This is where HolmesGPT, a CNCF Sandbox project, could help.
HolmesGPT was accepted as a CNCF Sandbox project in October 2025. It’s built to simplify the chaos of production debugging – bringing together logs, metrics, and traces from different sources, reasoning over them, and surfacing clear, data-backed insights in plain language.
What is HolmesGPT?
HolmesGPT is an open-source AI troubleshooting agent built for Kubernetes and cloud-native environments. It combines observability telemetry, LLM reasoning, and structured runbooks to accelerate root cause analysis and suggest next actions.
Unlike static dashboards or chatbots, HolmesGPT is agentic: it actively decides what data to fetch, runs targeted queries, and iteratively refines its hypotheses – all while staying within your environment.
Key benefits:
- AI-native control loop: HolmesGPT uses an agentic task list approach
- Open architecture: Every integration and toolset is open and extensible, works with existing runbooks and MCP servers
- Data privacy: Models can run locally or inside your cluster or on the cloud
- Community-driven: Designed around CNCF principles of openness, interoperability, and transparency.
How it works
When you run:
holmes ask “Why is my pod in crash loop back off state” HolmesGPT:
- Understands intent → it recognizes you want to diagnose a pod restart issue
- Creates a task list → breaks down the problem into smaller chunks and executes each of them separately
- Queries data sources → runs Prometheus queries, collects Kubernetes events or logs, inspects pod specs including which pod
- Correlates context → detects that a recent deployment updated the image
- Explains and suggests fixes → returns a natural language diagnosis and remediation steps.
Here’s a simplified overview of the architecture:
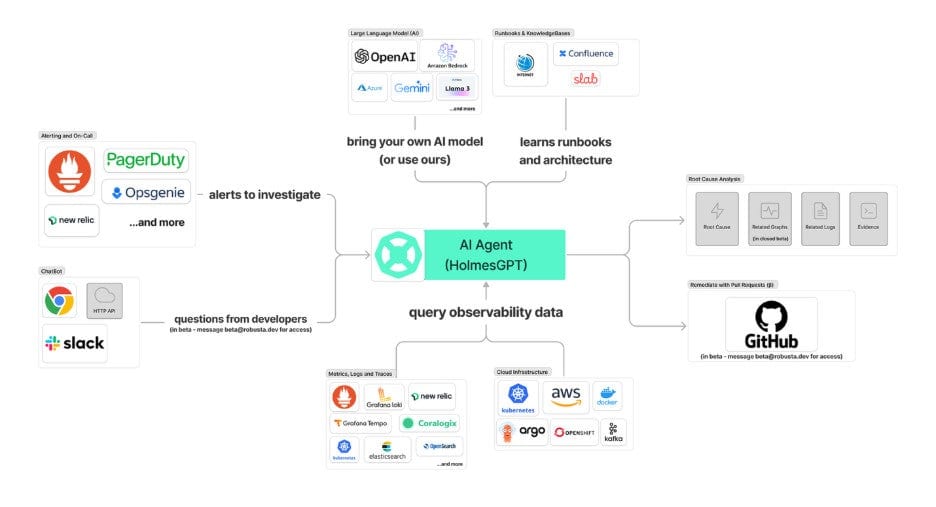
Extensible by design
HolmesGPT’s architecture allows contributors to add new components:
- Toolsets: Build custom commands for internal observability pipelines or expose existing tools through a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server.
- Evals: Add custom evals to benchmark performance, cost , latency of models
- Runbooks: Codify best practices (e.g., “diagnose DNS failures” or “debug PVC provisioning”).
Example of a simple custom tool:
holmes:
toolsets:
kubernetes/pod_status:
description: "Check the status of a Kubernetes pod."
tools:
- name: "get_pod"
description: "Fetch pod details from a namespace."
command: "kubectl get pod {{ pod }} -n {{ namespace }}"
Getting started
- Install Holmesgpt
There are 4-5 ways to install Holmesgpt, one of the easiest ways to get started is through pip.
brew tap robusta-dev/homebrew-holmesgpt
brew install holmesgpt
The detailed installation guide has instructions for helm, CLI and the UI.
- Setup the LLM (Any Open AI compatible LLM) by setting the API Key
In most cases, this means setting the appropriate environment variable based on the LLM provider.
- Run it locally
holmes ask "what is wrong with the user-profile-import pod?" --model="anthropic/claude-sonnet-4-5"
- Explore other features
- GitHub: https://github.com/robusta-dev/holmesgpt
- Docs: holmesgpt.dev
How to get involved
HolmesGPT is entirely community-driven and welcomes all forms of contribution:
| Area | How you can help |
| Integrations | Add new toolsets for your observability tools or CI/CD pipelines. |
| Runbooks | Encode operational expertise for others to reuse. |
| Evaluation | Help build benchmarks for AI reasoning accuracy and observability insights. |
| Docs and tutorials | Improve onboarding, create demos, or contribute walkthroughs. |
| Community | Join discussions around governance and CNCF Sandbox progression. |
All contributions follow the CNCF Code of Conduct.
Further Resources
- GitHub Repository
- Join CNCF Slack → #holmesgpt
- Contributing Guide